I want the HWND and HINSTANCE of a console window. How do I get it?
NOTE: A few comments at the bottom of this post have pointed out the existence of several functions that actually make this easier than I have shown here: particularly HWND hwnd = GetConsoleWindow();. There’s also GetModuleHandle(), used as Hardijzer mentions in the comments below, thought I might not have used this had I been aware of it. The complete listing of console functions is here on msdn.
Its actually easy! The short of it is:
// console app
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
char title[500]; // to hold title
// get title of console window
GetConsoleTitleA( title, 500 );
// get HWND of console, based on its title
HWND hwndConsole = FindWindowA( NULL, title );
// get HINSTANCE of console, based on HWND
HINSTANCE hInstance = (HINSTANCE)GetWindowLong(hwndConsole, GWL_HINSTANCE);
//alternate way
HWND hwndC = GetConsoleWindow() ; /* Great!! This function
cleverly "retrieves the window handle
used by the console associated with the calling process",
as msdn says */
// Then we could just get the HINSTANCE:
HINSTANCE hInstC = GetModuleHandle( 0 ) ; // HMODULE=HINSTANCE
//HINSTANCE hInstCons = (HINSTANCE)GetWindowLong( hwndC, GWL_HINSTANCE );
}
See msdn article on FindWindow function.
The GetWindowLong() function, in the msdn spotlight.
We now have the HWND of the console in variable hwndConsole, and the HINSTANCE of the console window in hInstance.
Now, you COULD create a window up, because you have the HINSTANCE now. The example below illustrates the “long” of it:
//////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// Getting the HWND of the Console //
// //
// You found this at bobobobo's weblog, //
// https://bobobobo.wordpress.com //
// //
// Creation date: Feb 3/08 //
// Last modified: Feb 3/08 //
// //
//////////////////////////////////////////
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <windows.h>
// So you need the handle (HWND) for the
// console window for your app.
// Who knows why. Maybe ya just
// want it.
///////////////////////////////
// In this example, I'm:
// 1) using the HWND of the console window
// to get the HINSTANCE of the console window
// (GetWindowLong() function)
//
// 2) using the HINSTANCE and HWND of the
// console window to create a regular
// window with a WndProc and a message
// loop and all (WNDCLASS structure,
// RegisterClass(), then CreateWindow())
// based off of MSDN KB article
// http://support.microsoft.com/kb/124103
// prototype for the WndProc of the window that
// we're gonna create.
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc( HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wparam, LPARAM lparam );
/////////////////
// Normally, windowed apps would start
// at WinMain().
// However, remember that this is REALLY
// a console application, and we're just
// spawning a window out of it.
// This application starts at first line of main().
int main()
{
// console window exists as soon as app start
// get its hwnd using combo of "GetConsoleWindowTitle()"
// and "FindWindow()"
// Why did i call this _REGION_A_? see end notes!
#pragma region _REGION_A_ - get HWND of console
char t[500];
GetConsoleTitleA( t, 500 ); // retrieve the text
// of the title bar of the console window
cout << "The title of the console window is:" << endl;
cout << t << endl << endl;
HWND hwndConsole = FindWindowA( NULL, t ); // FindWindowA actually
// can get you the HWND of a window, based
// on the text in its title bar!
// Let's check to see it worked. If the console window
// moves after the function call below, then we know
// that hwndConsole is really a valid handle to the console
// window!
MoveWindow( hwndConsole, 20, 20, 500, 500, true ); // test hwnd
#pragma endregion
#pragma region _REGION_B - get HINSTANCE and create a window!
////////////////////////
// Getting the HINSTANCE given the HWND
//
// Want the HINSTANCE of a window, but
// you only have its HWND?
//
// Here's how you generally get the HINSTANCE
// of the console, based off of the HWND of
// the console.
HINSTANCE hInstance = (HINSTANCE)GetWindowLong(hwndConsole, GWL_HINSTANCE);
////////////////////
// Now I'm going to create an ACTUAL WINDOW.
//
// Note that you always need a HINSTANCE
// to create a window, which is why I just
// got it in the line just above here.
WNDCLASS wc = {0};
wc.hbrBackground =(HBRUSH)GetStockObject(WHITE_BRUSH);
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor( hInstance, IDC_ARROW );
wc.hIcon = LoadIcon( hInstance, IDI_APPLICATION );
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.lpszClassName = TEXT("peter"); // name of window class .. I choose peter
wc.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW;
if (! RegisterClass( &wc ) )
{
cout << "Problem with your WNDCLASS, foo." << endl;
return 1; // ERR, SO QUIT
}
// Create a real live window!
// (see https://bobobobo.wordpress.com/2008/01/31/how-to-create-a-basic-window-in-c/
// for more details on basic windows)
HWND hwndWindow = CreateWindow( TEXT("peter"),
TEXT("the window"),
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,
520, 20, 300, 300,
NULL, // if you make this hwndConsole, then
// the console becomes this window's parent
// Then, this window wouldn't get an
// entry in the taskbar
NULL,
hInstance, NULL );
ShowWindow( hwndWindow, SW_SHOWNORMAL ); // ShowWindow() on msdn
UpdateWindow( hwndWindow );
#pragma endregion
// Enter regular message loop, to process messages for
// our window.
#pragma region _REGION_C - message loop
MSG msg;
while( GetMessage( &msg, hwndWindow, 0, 0 ) )
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
#pragma endregion
return msg.wParam;
}
////////////
// The WndProc for the Window that
// we eventually open up
// (This WndProc is _NOT_ FOR THE CONSOLE WINDOW!)
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc( HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wparam, LPARAM lparam )
{
switch( message )
{
case WM_CREATE:
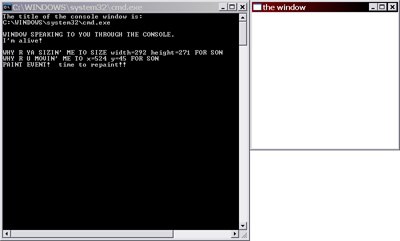
cout << "WINDOW SPEAKING TO YOU THROUGH THE CONSOLE." << endl;
cout << "I'm alive!" << endl << endl;
Beep( 40, 40 );
return 0;
break;
case WM_PAINT: // paint event
{
cout << "PAINT EVENT! time to repaint!!" << endl;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc;
BeginPaint( hwnd, &ps );
EndPaint( hwnd, &ps );
return 0;
}
break;
case WM_LBUTTONDOWN: // left clicking on the client area of the window (white part)
cout << "WHY R YA MOUSE DOWN'IN ME AT x=" << LOWORD(lparam) << " y=" << HIWORD(lparam) << " SON" << endl;
return 0;
break;
case WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN: // NONCLIENT area leftbutton down (click on "title bar" part of window)
//cout << "AAAH!! YER GONNA MOVE ME SON. CAREFUL SON." << endl;
//return 0; // this is an interesting one.
// try UNCOMMENTING the return 0; statement here.
// Notice that you can NO LONGER move or manipulate
// the window by clicking on its "title bar"
// if you return 0; from here. The reason for that
// is the window movement is actually handled by
// DefWindowProc(). That's why its so important
// to remember to pass events you don't handle to
// DefWindowProc() -- if you don't then the Window
// won't act in the "default" way you're so used to
// other windows acting in (in fact, it won't even
// show up properly)
break;
case WM_CHAR: // character key
cout << "WHY R U CHARRING ME WITH " << (char)wparam << " FOR SON" << endl;
return 0;
break;
case WM_MOVE: // moving the window
cout << "WHY R U MOVIN' ME TO x=" << LOWORD(lparam) << " y=" << HIWORD(lparam) << " FOR SON" << endl;
return 0;
break;
case WM_SIZE:
cout << "WHY R YA SIZIN' ME TO SIZE width=" << LOWORD(lparam) << " height=" << HIWORD(lparam) << " FOR SON"<< endl;
return 0;
break;
case WM_DESTROY: // killing the window
cout << "NOOO!! I . . . shall . . . return !!" << endl;
PostQuitMessage( 0 );
return 0;
break;
}
return DefWindowProc( hwnd, message, wparam, lparam );
}
////////////////////////
// END NOTES:
//
// If you read the MSDN article carefully,
// it says some shit about wanting to
// SetConsoleTitle( "stupid unique title");
// The reason for that is, there is an OFF
// CHANCE that PERHAPS there's more than one
// window with the same exact TITLE
// as our console window.
//
// There's a bit of code at the bottom of the
// Visual Studio project files that shows
// how to do that.
//
/*
____ __ __ __ __ ___
/ _ \ / / / / / / \ \/ /
/ _/ / / / / / / / \ /
/ _/ \ / / / /__ / /__ / /
/_____//__/ /______//______/ /__/
*/
Visual Studio 2005 project files, hosted by esnips (thanks esnips!)
10 Comments
after WM_DESTROY is called, the PostQuitMessage causes the GetMessage to result in an error (ERROR_INVALID_WINDOW_HANDLE). Any idea why this happens?
how can I now use the console window to accept user input? thanks for your example, it is very helpful.
There is no quick method to get the HWND of the console window. *however*, for your end gain of getting a HINSTANCE, you should try (HINSTANCE)GetModuleHandle(0). It’s much more robust and failsafe.
Basically a HMODULE and a HINSTANCE are interchangable, and GetModuleHandle(0) gets the HMODULE of the module (executable) used to create the current process.
Try:
hWnd = GetConsoleWindow () ;
Well in a fast read your way is compatible with older win OS, but as shown in the two previous comments, using GetConsoleWindow () and GetModuleHandle(NULL) is much easier isn’t it? ;-)
yea, you’re right. updating the post now!
man you are the greatest thanx a lot
Are your sure that GetWindowLong(hwndConsole, GWL_HINSTANCE) can retrive hInstance correctly? I always get 0 …
I found just let hInstance = 0 also works.
I’m using Win 7 x86.
This is a great tutorial.
I easily converted to C and it completely served my purpose.
Using win-xp, no problem.
Thanks.
This is way cool, thankyou. But, on my confuser this statement
while( GetMessage( &msg, hwndWindow, 0, 0 ) )
results in an infinite message loop when I close the daughter window, hogs 99% of my 1 CPU, Ctrl-Break does close the console…
whereas
while (GetMessage(&msg, hwndWindow, 0, 0) > 0)
exits correctly
I’m using Code::Blocks and gcc on widdoze xp